[Vue] Virtual DOM은 대체 무엇인가
우리는 Vue.js와 React가 virtual DOM 을 제공하기 때문에 보다 빠르고 효율적인 UI 렌더링이 가능한 것으로 알고 있습니다. 하지만 추상적으로만 알고 있던 Virtual DOM에 대해 자세히 답할 자신이 없었고, 이 참에 찾아본 자료를 공유하고자 합니다.
카테고리를 React와 Vue 어디에 넣어야 할지 고민했습니다. 그 결과 제가 Vue를 더욱 먼저 배웠고, 이 때 적어둔 자료이기 때문에 Vue 카테고리로 분류하기로 하였습니다.
📌 Virtual DOM의 필요성
DOM(Document Object Model) 은 HTML document를 객체 기반적으로 추상화한 것이고, 이를 통해 우리는 객체로써의 DOM과 상호작용하며 쉽게 조작을 할 수 있다.
만약 DOM 트리에 있는 수 많은 elements 중 특정 엘레먼트의 text를 바꾸고자 할 때, 우리는 document.getEelementBy~ 또는 document.querySelector 라는 DOM API를 통해 해당 elements를 가져오고, document.createElement() 를 통해 만든 새로운 element로 교체할 것이다. 다음의 html 구성을 보자.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head></head>
<body>
<ul class="list">
<li class="list__item">List item</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
위의 HTML document는 다음의 DOM Tree로 표현할 수 있다.
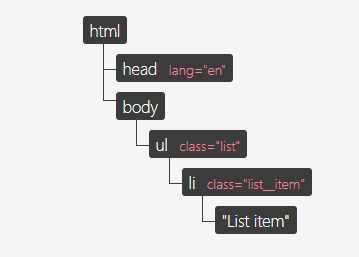
만약 li 중 첫 번째 li의 textContent 를 ‘list item one’ 으로 변경하고 싶다면, 우리는 새로운 element를 생성하고, element에 textContent attribute를 추가해야 하며, 마지막으로 DOM elements를 교체(update)해야 한다. DOM API를 사용해 다음과 같은 코드를 작성해야 할 것이다.
const listItemOne = document.getElementsByClassName('list__item')[0];
listItemOne.textContent = 'List item one';
const list = document.getElementsByClassName('list')[0];
const listItemTwo = document.createElement('li');
listItemTwo.classList.add('list__item');
listItemTwo.textContent = 'List item two';
list.appendChild(listItemTwo);
하지만 document.getElementByClassName() 은 소규모의 DOM에서는 잘 동작하지만, 다양한 elements를 가진 페이지에서 하나의 element를 이와 같이 update한다면, 굉장히 큰 비용이 발생한다.
javascript로 DOM을 조작하게 된다면, 각 변경사항 마다 하나씩 해석해 렌더링을 시키게 된다. 이때 렌더링 비용이 상당히 소요된다고 한다.
따라서 하나의 element를 update하는 것보다는 더욱 큰 부분을 update하는 것이 보다 적은 비용이 소요된다. 다음의 코드를 보자.
const list = document.getElementsByClassName('list')[0];
list.innerHTML = `
<li class="list__item">List item one</li>
<li class="list__item">List item two</li>
`;
📌 Virtual DOM이란?
우리는 위와 같이 DOM을 빈번히 update해야 하는 상황에 자주 직면한다. Virtual DOM은 이런 상황에 효율적이다. React 에 채택되며 유명해지게 된 Virtual DOM은 공식 스펙은 아니지만, DOM과 상호작용하는 새로운 방식이다.
Virtual DOM은 실제 DOM의 copy 개념이다. 이 copy는 실제 DOM API를 호출하지 않고, 빈번하게 조작 및 변경된다. 모든 변경이 Virtual DOM 에 반영이 된 후, 실제 DOM을 효율적으로 변경한다.

위의 DOM tree를 JS Object로 표현한다면 다음과 같다.
const vdom = {
tagName: 'html',
children: [
{ tagName: 'head' },
{
tagName: 'body',
children: [
{
tagName: 'ul',
attributes: { class: 'list' },
children: [
{
tagName: 'li',
attributes: { class: 'list__item' },
textContent: 'List item',
}, // end li
],
}, // end ul
],
}, // end body
],
}; // end html
위의 JS Object를 Virtual DOM이라 생각하면 된다. JS Object이기 때문에 실제 DOM API의 호출 없이 자유롭게 조작하고 update할 수 있다.
실제 Virtual DOM은 전체가 아닌 작은 영역들로 분할되어 작업되는 것이 일반적이다. 위에서는 list의 update와 추가를 했기 때문에 다음과 같이 쪼개질 수 있다.
const list = {
tagName: 'ul',
attributes: { class: 'list' },
children: [
{
tagName: 'li',
attributes: { class: 'list__item' },
textContent: 'List item',
},
],
};
이 list object가 어떻게 변경되는지 살펴보자.
- List item → List item one 으로 변경
- 두 번째 List 요소 추가
위의 list object(Virtual DOM)의 copy가 생성되며, 두 가지 작업 내역이 반영된다.
const copy = {
tagName: 'ul',
attributes: { class: 'list' },
children: [
{
tagName: 'li',
attributes: { class: 'list__item' },
textContent: 'List item one', // 이름 변경
},
// 아래 객체 추가
{
tagName: 'li',
attributes: { class: 'list__item' },
textContent: 'List item two',
},
],
};
이 Virtual DOM의 복사본과 Virtual DOM을 비교해 실제 달라진 부분을 비교하는 diff를 만들 수 있다.
const diffs = [
{
newNode: { /* new version of list item one */ },
oldNode: { /* original version of list item one */ },
index: /* index of element in parent's list of child nodes */
},
{
newNode: { /* list item two */ },
index: { /* */ }
}
]
이 diff는 변경사항을 반영하기 위해 실제 DOM을 어떻게 변경해야할 지 보여준다. 모든 diff들이 생성되면, diffs 로 묶어 일괄적으로 DOM을 변경할 수 있다.
예를 들면 diffs를 loop문 돌면서, 새로운 자식 요소를 추가하거나 업데이트 할 수 있다.
const domElement = document.getElementsByClassName('list')[0];
diffs.forEach(diff => {
const newElement = document.createElement(diff.newNode.tagName);
/* Add attributes ... */
if (diff.oldNode) {
// If there is an old version, replace it with the new version
domElement.replaceChild(diff.newNode, diff.index);
} else {
// If no old version exists, create a new node
domElement.appendChild(diff.newNode);
}
});
요약
최근의 웹 페이지의 규모가 클수록 많은 element들을 갖고 있고, 빈번하게 update되고, 조작된다. DOM API를 통해 직접 DOM 요소에 접근해 이와 같은 작업을 진행한다면, 상당한 비용이 소요된다.
직접 DOM API를 호출하지 않고, Virtual DOM에 변경사항을 반영한 후, 실제 DOM 과 Virtual DOM 을 비교해 달라진 부분만 조작함으로써 보다 빠르고 효율적으로 DOM을 그려낼 수 있다.

Leave a comment